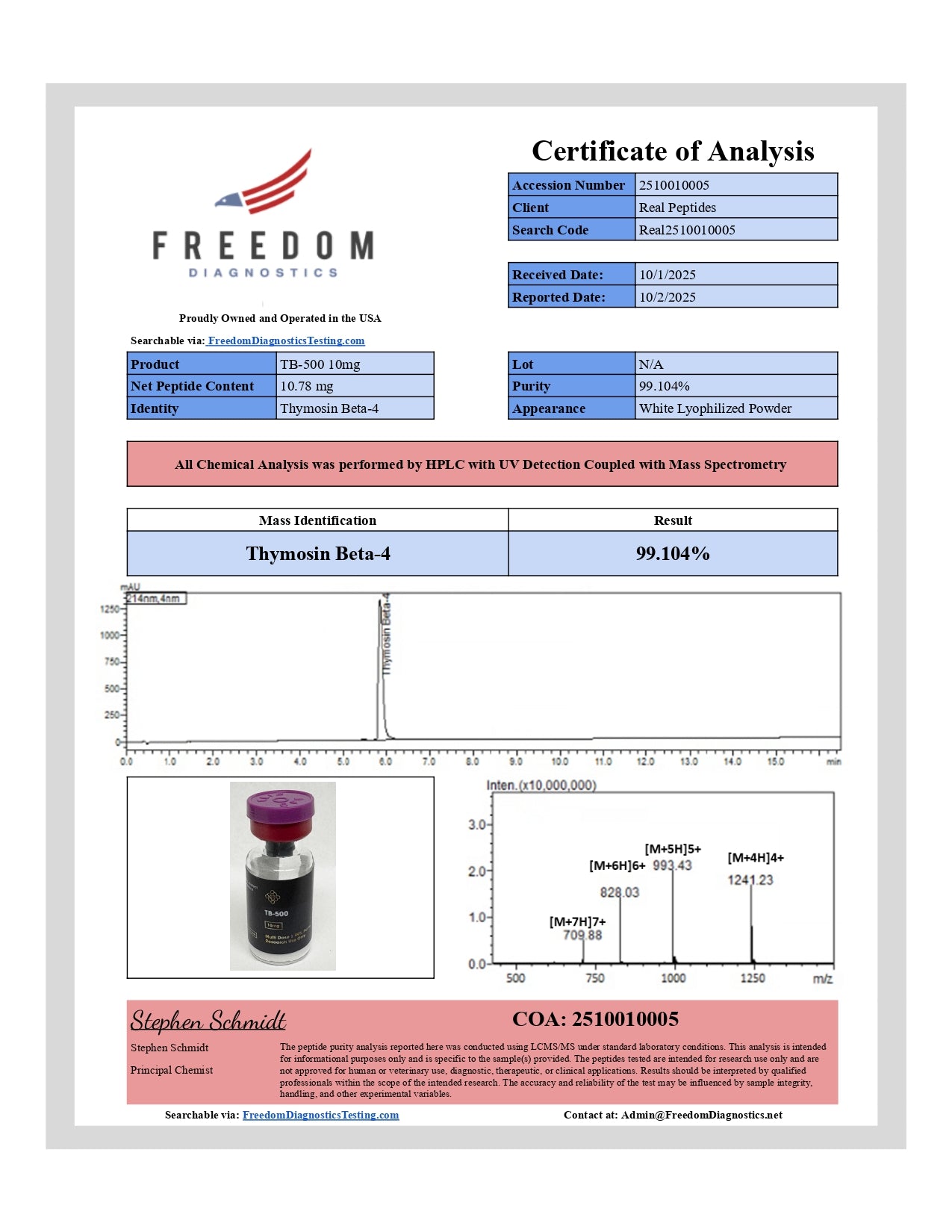




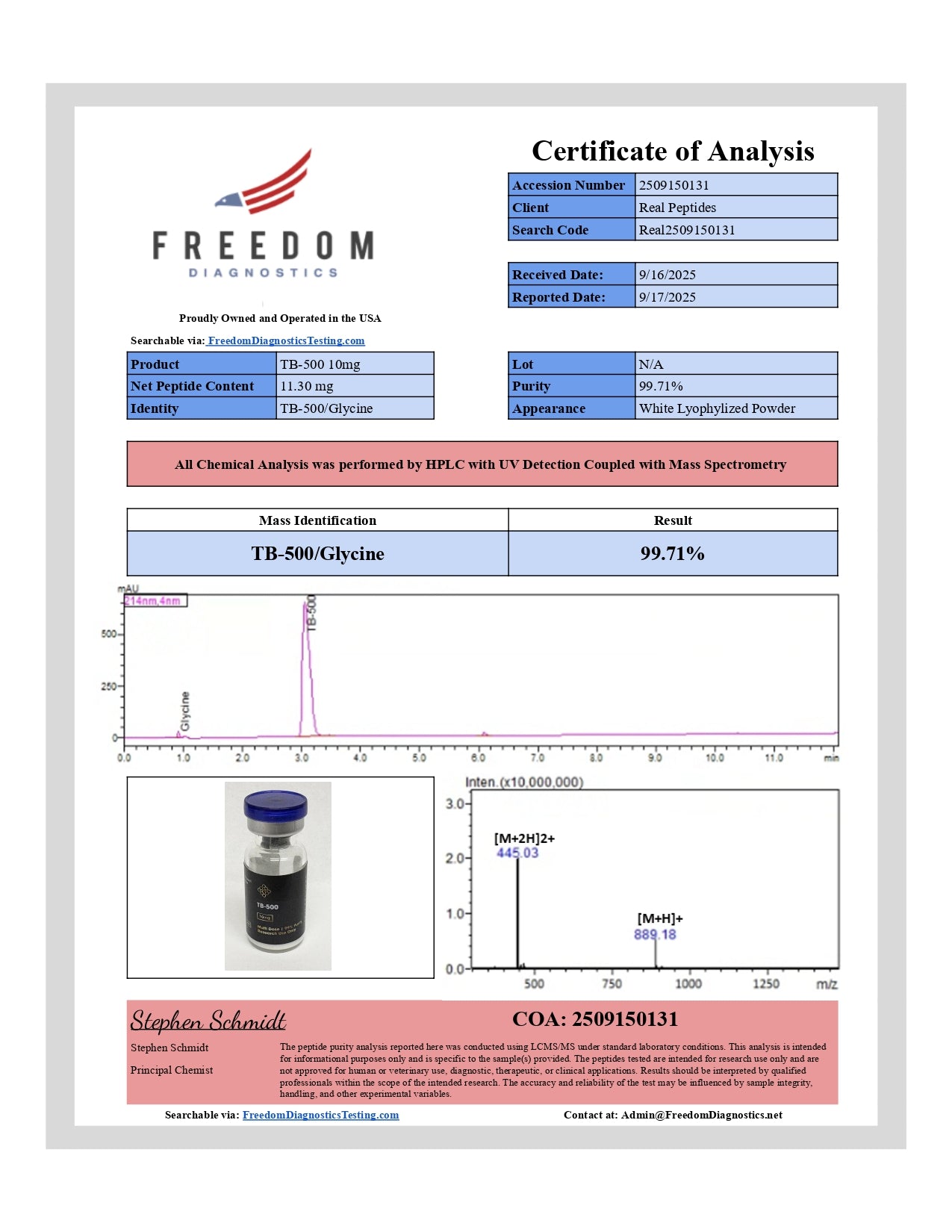
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4)
TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4) is a synthetic 43-amino-acid peptide fragment used in preclinical models to explore tissue repair, cell migration, and inflammation resolution. In cell-culture wound-closure assays and rodent injury models, TB-500 accelerates fibroblast migration, modulates cytokine profiles, and supports angiogenic signaling. Each 10 mg vial is USA-manufactured, HPLC-verified to ≥ 99% purity, endotoxin-screened (< 0.1 EU/mg), and formulated for laboratory research.
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
For Research Use Only. Not for human consumption or therapeutic treatment.
Pairs well with
Peptides are not ready to use. Must purchase BAC water for reconstitution.

TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4)
TB-500
Accelerated Wound Closure
TB-500 peptide enhances fibroblast and keratinocyte migration in scratch assays—reducing gap closure time by up to 60%.
Angiogenesis Promotion
Upregulates VEGF and promotes capillary-tube formation in endothelial cultures, modeling blood-vessel growth.
VEGF-Mediated Angiogenesis
In endothelial cultures, TB-4 increases VEGF expression and capillary tube formation, enabling detailed microvascular growth studies.
Anti-Inflammatory Modulation
Downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) in macrophage assays, supporting inflammation-resolution studies.
Cell-Stress Resilience
Improves cell survival under oxidative or hypoxic stress by boosting mitochondrial function markers (ATP, membrane potential).
Extracellular Matrix Remodeling
Increases expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-2, MMP-9) in fibroblasts, aiding studies of ECM turnover and tissue remodeling.
Lab-Grade Handling & Stability
TB-4 dissolves readily in SWFI or BAC water, remains stable lyophilized at –20 °C, and retains >99% integrity when stored reconstituted at 2–8 °C for up to 7 days.

What is TB-500?
TB-500, also called TB500 or Thymosin Beta-4 peptide, is a synthetic fragment of the naturally occurring Thymosin β4 protein. It plays a key role in actin-binding, cell-migration, and repair signaling. In research contexts, TB-500 is applied to both in vitro and in vivo models to dissect pathways of tissue regeneration, angiogenesis, and inflammation resolution.

Why Choose TB-500 Peptide?
Researchers select TB-500 when they need a versatile tool for modeling wound healing, vascular growth, and anti-inflammatory effects in controlled experiments. Its proven effect in accelerating cell migration and promoting capillary formation—coupled with strict ISO-certified manufacturing and ≥ 99% purity—ensures reproducible, high-quality data for regenerative-medicine and tissue-repair studies.

What Sets TB-500 Apart?
Unlike broader growth-factor agents, TB-500 peptide offers precise modulation of both cytoskeletal dynamics and angiogenic signaling via its actin-binding properties. Its dual action on cell migration and inflammation resolution, plus demonstrated stability in solution, makes TB-500 the go-to peptide for high-resolution studies of tissue repair and regenerative pathways.
TB-500 FAQs
What is TB500 (TB4) peptide?
TB500 is a synthetic Thymosin Beta-4 fragment used to study wound healing, cell migration, and angiogenesis.
Is TB-500 the same as Thymosin Beta-4?
TB500 is a synthetic peptide fragment of the full Thymosin β4 protein, designed for research applications.
How does TB-500 accelerate healing?
By enhancing fibroblast and keratinocyte migration and upregulating VEGF, TB-500 speeds gap closure and blood-vessel growth.
Can TB-4 be combined with other peptides?
Yes. TB-4 is often co-studied with peptides like BPC-157, GHK-Cu, or growth factors to assess synergistic effects on repair.
Can TB-500 reduce inflammation?
Yes—TB-500 downregulates IL-6 and TNF-α in macrophage models, aiding inflammation-resolution research.
Is TB-4 stable at room temperature?
Lyophilized TB-4 should be stored at –20 °C; reconstituted solutions are best kept at 2–8 °C and used within 7 days.
Does TB-4 promote blood-vessel formation?
Yes. Preclinical studies show TB-4 enhances VEGF expression and capillary network formation in endothelial assays.
What are TB-4’s anti-inflammatory effects?
TB-4 modulates IL-6 and TNF-α levels in macrophage cultures, offering a research tool for inflammation-resolution studies.
Is TB-4 approved for therapeutic use?
No. TB-4 is strictly for research use only and is not approved for human or veterinary treatment.
Where can I buy TB-500 peptide?
Real Peptides offers ISO-certified, USA-made TB-500 (10 mg) at ≥ 99% purity and low endotoxin—available for research use only.